All types of solar panels explained: A comprehensive guide
Curious about the different types of solar panels out there? With so many options available, choosing the right one for your home can feel a bit overwhelming. Solar technology has come a long way, so understanding the differences between panel types is your key to making a sound decision.
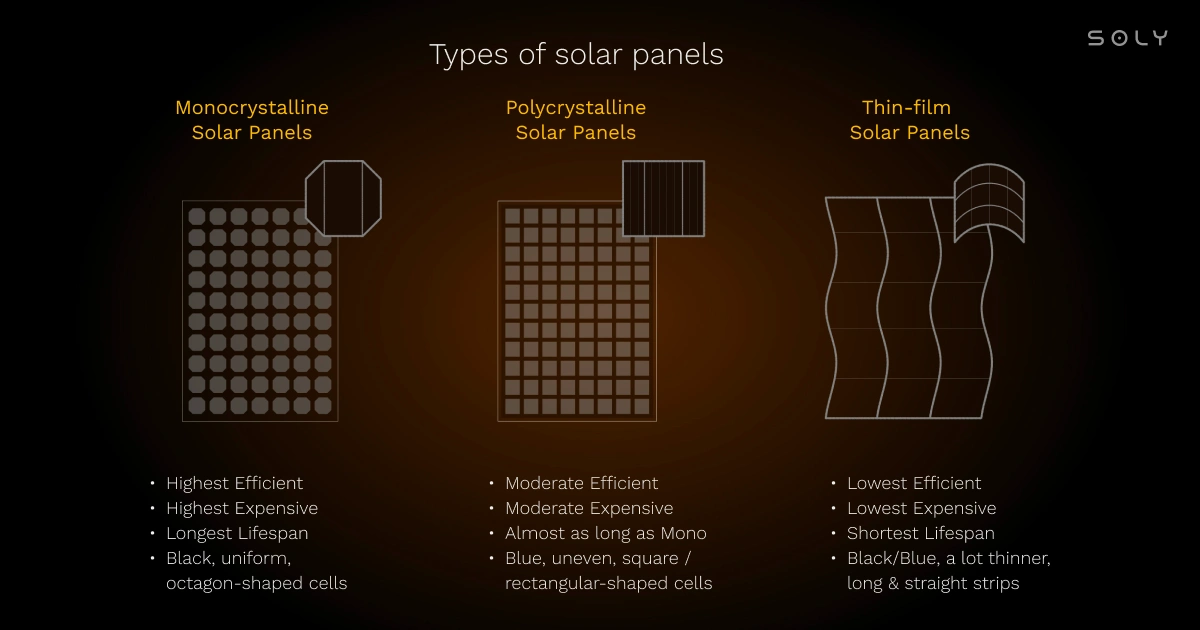
The three main types of solar panels on the market today include monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film. Each of these come with their own distinct benefits, depending on your energy needs and budget.
That said, energy prices are continuing to surge in the UK and solar panels are very much the enticing solution that many households have been searching for. It could allow them to slash costs and shrink their carbon footprint all at the very same time. In fact, by July of 2024, the UK had installed an impressive 17 gigawatts (GW) of solar capacity.
Without a doubt, this surge unveils that more and more homeowners are beginning to make their way toward renewable energy like solar so that they can once and for all regain control over their energy bills and make way for a greener tomorrow. Solar is undeniably becoming a savvy financial move for many.
On this page you’ll learn:
- All about 1st, 2nd, and 3rd generation solar panels
- The latest solar panels with innovative applications
- How to choose the best solar panel for your home
When you’re choosing to install solar panels, there’s a few things you’ll need to consider before you take the leap into solar. As experts on all things solar, allow us to be your guide. The types of solar panels work to absorb light in their own way, which is precisely what we’re about to uncover.
Let’s begin!
- Introduction to solar panel types
- Different types of solar panels by generation explained
- 1st Generation solar panels (crystalline technology)
- 2nd Generation solar panels (thin-film technology)
- 3rd Generation solar panels (the next generation)
- Latest solar panels with innovative applications & technologies
- Choosing the best solar panel for your home
- FAQ
- Final Verdict: Which is the best type of solar panel?
Introduction to solar panel types
Understanding solar cell generations
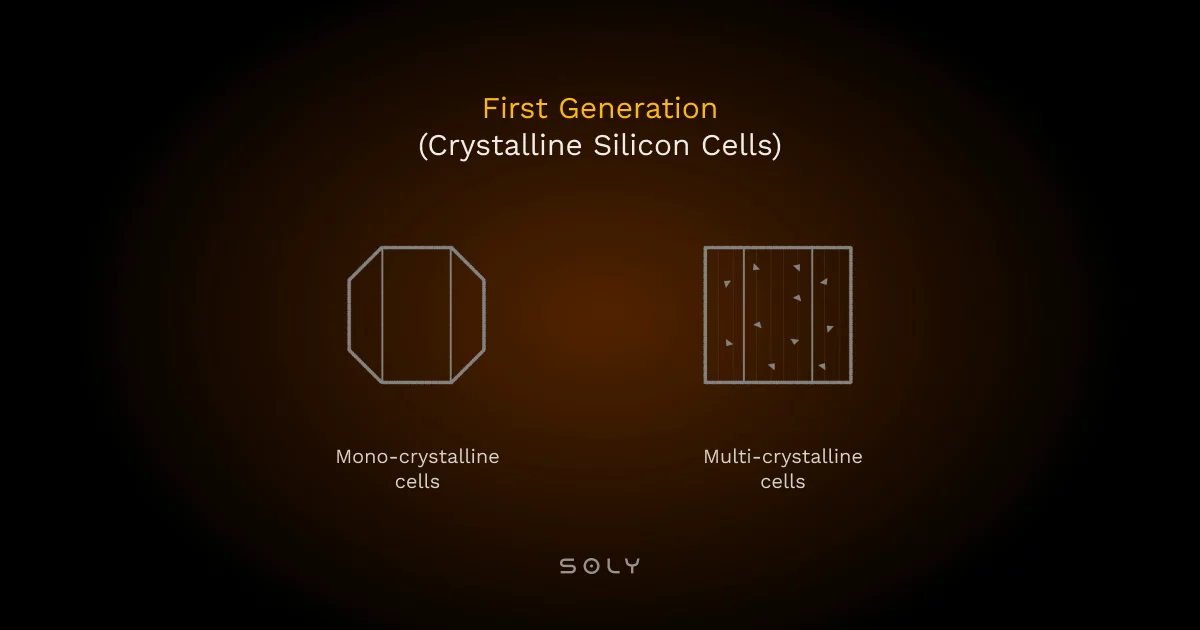
First-generation solar cells: Out of all the types of solar cells, the 1st generation cells are the ones you commonly spot on rooftops.
- They include standard monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels crafted from silicon.
- While monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels do a solid job of converting sunlight into electricity, their energy efficiency has a cap.
- Though reliable and widely adopted, they fall short of the energy output delivered by newer solar technologies.
Second-generation solar cells: These cells harness materials different from the traditional crystalline silicon panels.
- They’re thinner, lighter, and more adaptable, making them more affordable and versatile.
- Thanks to their lightweight design, they can be deployed in a broader range of applications.
However, they don’t pack the same punch as the first-generation models. It’s like opting for a budget-friendly car instead of a high-performance sports car. The budget car will get you where you need to go, but it won’t deliver the same power.
While second-generation solar cells are lighter, more flexible, and easier on the wallet, their efficiency still falls short of their first-generation counterparts.
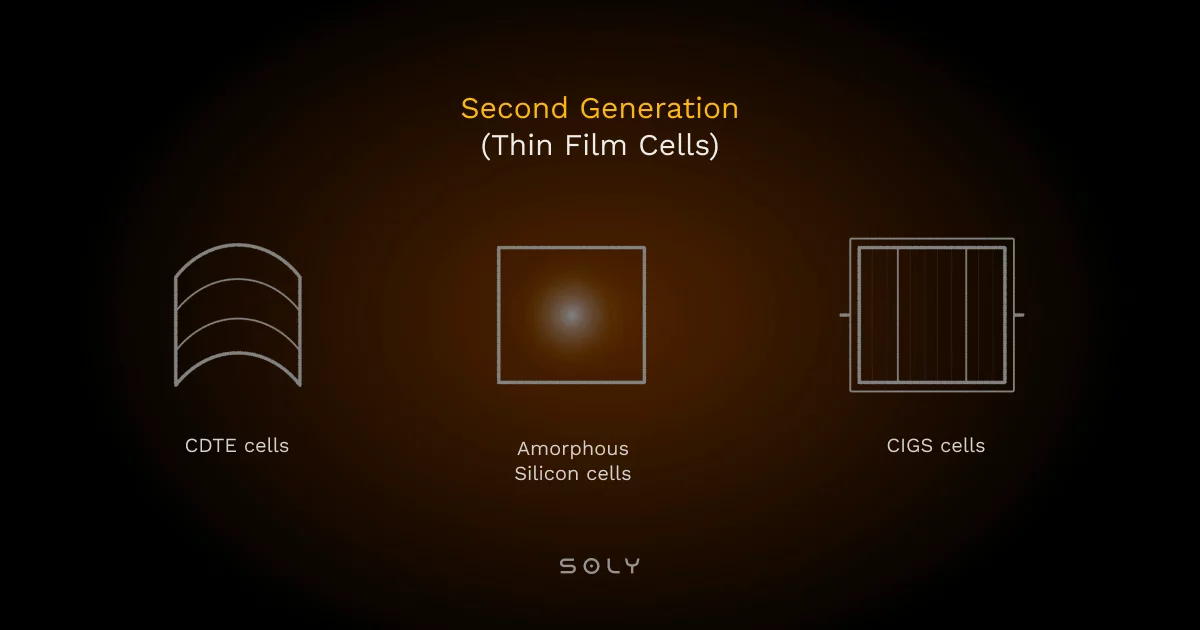
Some of the most commonly available thin film solar technologies include:
- Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS) is a highly flexible and efficient thin-film solar technology that’s great at capturing sunlight. This makes it perfect for specialised uses. This includes things like integrating solar panels directly into building materials such as windows or roofs.
- Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) is a popular thin-film solar technology. The cadmium telluride solar cell is highly valued for being both affordable and efficient. This is especially the case in low-light conditions. However, because it contains cadmium, a toxic material, there are environmental concerns about its disposal and long-term impact.
- Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) is highly efficient and thrives in extreme conditions. This makes it perfect for specialised applications. This includes things like space technology. Its exceptional efficiency makes it a go-to for generating power in situations where other solar technologies might struggle.
- Amorphous Silicon (a-Si) is a lightweight, flexible material used in thin-film solar panels. Unlike traditional silicon, it’s non-crystalline, making it easier to apply to different surfaces. However, its lower efficiency means it produces less power from the same amount of sunlight compared to crystalline panels.
Third-generation solar cells: 3rd gen solar cells are the next-level evolution of traditional solar panels. Think of them as a futuristic leap forward.
These cells harness advanced materials and innovative techniques to capture more sunlight and convert it into electricity with far greater efficiency. Representing the pinnacle of solar technology, they hold immense potential for delivering higher energy output and enhanced performance compared to earlier versions.

Here’s how these innovative panels work:
- Multi-layer (Tandem) cells: Picture a club sandwich, with each layer designed to capture different parts of sunlight. One layer snatches red light, while another grabs blue, making the whole system more efficient.
- Frequency conversion: Imagine wearing sunglasses that transform sunlight into a form your solar panel can better absorb. This technology helps convert otherwise unusable light into energy.Hot-carrier effects: Think of this as catching energy that would normally escape, like harnessing steam from boiling water to generate electricity. It’s about squeezing extra power from high-energy electrons that would otherwise be lost.
Now, let’s look at new and emerging solar cell types:
- CZTS (Copper Zinc Tin Sulfide) solar cells are crafted from a blend of inexpensive, readily available materials. Though still in development, they hold promise for being both affordable and adaptable—like swapping out costly ingredients for more common ones in a recipe.
- Dye-sensitised solar cells (Grätzel Cells) function similarly to how our eyes perceive colours, using dyes to capture the sun’s rays and then convert it into electricity. They’re flexible, come in different colours, and are perfect for creative designs.
- Organic solar cells are carbon-based cells that can be printed like ink on various surfaces. Think of them as solar panels you can roll up or use in lightweight, wearable tech.
- Perovskite solar cells are built from a unique crystal structure, they offer high efficiency and are cheaper to produce, but researchers are still working on improving their lifespan. It’s like having a powerful tool that breaks easily. They’re trying to fix the durability issue.
- Quantum dot solar cells use minuscule particles that absorb specific wavelengths of sunlight, helping to capture more energy. It’s like tuning a radio to the right frequency for the clearest signal.
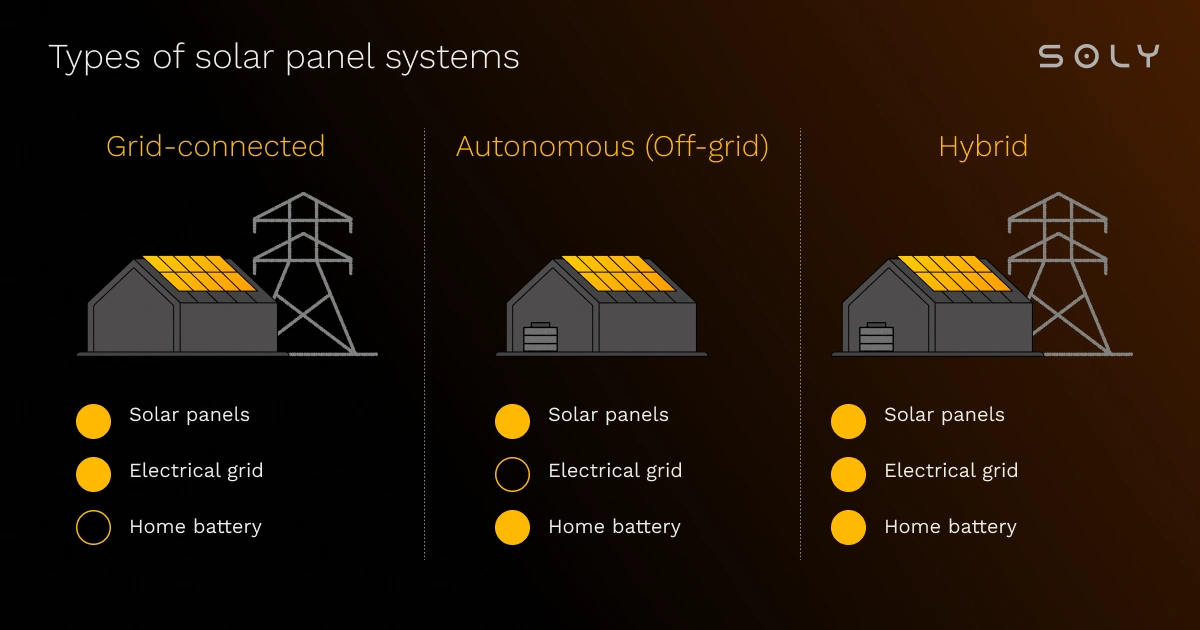
Understanding the types of solar panel systems
When it comes to understanding the different types of solar panel systems each offers different benefits, depending on your energy needs.
Let’s explore the options:
1. Grid-connected solar panel systems
These systems are directly linked to the grid. They allow you to tap into solar energy while still pulling power from the grid when needed. You can sell excess energy back to the grid through net metering and provides reliable access to power, even on cloudy days or at night.
Advantages:
- ✅ Saves on electricity bills by using solar energy first.
- ✅ Easy to install and maintain, with less components involved than other systems.
Disadvantages:
- ❌ Depends on the grid: If there’s a grid outage, your solar system shuts down too.
- ❌ Initial costs can be steep, but long-term savings help offset the investment.
2. Autonomous solar panel systems (Off-grid)
These systems run entirely off the grid. They store extra solar energy in batteries for use at night or during cloudy days. Autonomous solar panel systems are equipped with battery storage to capture unused energy and they’re ideal for remote locations or areas without grid access.
Advantages:
- ✅ Provides complete energy independence, with no reliance on utility companies.
- ✅ Reduces your carbon footprint by using only solar power.
Disadvantages:
- ❌ Higher upfront costs: Batteries and other components raise the initial price.
- ❌ Requires ongoing maintenance for both batteries and panels to keep everything running smoothly.
3. Hybrid solar panel systems
Hybrid systems blend the best of grid-tied and off-grid setups. They combine solar energy, battery storage, and grid access. They allow you to store energy in batteries for later use while still being connected to the grid.
Advantages:
- ✅ Flexibility to run independently during outages while still cutting electricity costs.
- ✅ Maximises efficiency by drawing power from solar, battery, and grid sources.
Disadvantages:
- ❌ More components mean a more complex installation.
- ❌ Higher upfront investment, though long-term savings often make it worthwhile.
Different types of solar panels by generation explained
Solar technology has undoubtedly come a long way. With many generations of solar panels now currently available, they each offer unique features that are suited to differing needs. Below, we take a look at these different types of solar panels by generation, availability, and key features, to help you make your decision.
| Solar Panel Type | Generation | Availability | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monocrystalline solar panels | 1st Generation | Commercially Available | High efficiency (20%+), long lifespan (25+ years), ideal for homes with limited roof space. |
| Polycrystalline solar panels | 1st Generation | Commercially Available | More affordable, lower efficiency (14%-16%), requires more roof space. |
| Thin-film solar panels (a-Si, CIGS, CdTe) |
2nd Generation | Commercially Available | Lightweight, flexible, lower efficiency (7%-13%), used in special applications (e.g., windows, vehicles). |
| Biohybrid solar panels | 3rd Generation | Developmental Phase | Mimics photosynthesis, combines biological elements with synthetic materials. |
| Concentrated PV Cells (CPV/HCVP) | 3rd Generation | Commercially Available | Uses lenses/mirrors to focus sunlight, very high efficiency (40%+), ideal for large-scale projects. |
| Perovskite solar panels | 3rd Generation | Developmental/Commercially Available | High efficiency, low-cost production, rapidly evolving with efficiency over 25%. |
| Organic Photovoltaics (OPVs) | 3rd Generation | Developmental Phase | Flexible, lightweight, made from organic materials, less efficient. |
| Quantum dot solar cells | 3rd Generation | Developmental Phase | Nanoscale semiconductors, highly efficient, promising for new applications like windows. |
| Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells (DSSCs) | 3rd Generation | Commercially Available | Low-cost, flexible, colorful panels, less efficient but ideal for niche uses. |
1st Generation solar panels (crystalline technology)
Monocrystalline solar panels
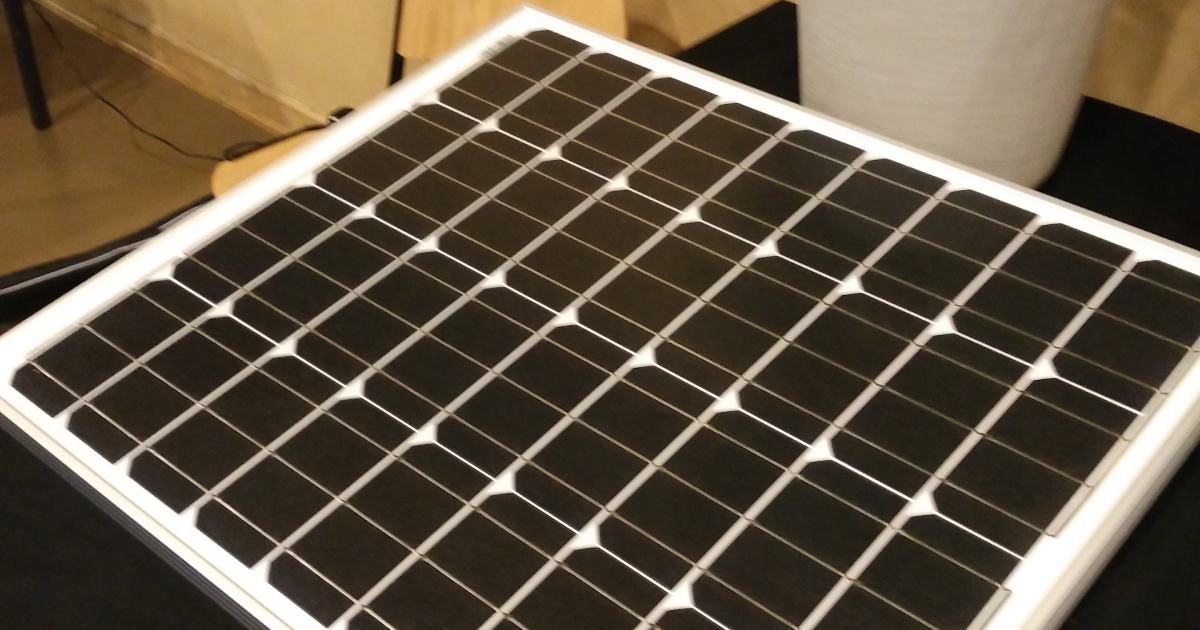

Monocrystalline solar panels are renowned for their exceptional efficiency and durability. This makes them among the most sought-after choices for many UK homeowners. Here’s why these solar panels work:
- Built from single-crystal silicon cells, they boast superior electron flow, leading to higher efficiency.
- These panels convert over 20% of sunlight into electricity. Due to their energy efficiency, they’re perfect for homes with limited roof space.
- They’re built to last, often with a lifespan exceeding 25 years.
- Their space-saving design means fewer panels are needed to generate the same power as other types.
- They excel in low light, making them ideal for the UK’s cloudy skies.
Monocrystalline solar panels are seen as the gold standard in solar technology.
For that reason, they’re quite literally perfect for homeowners looking to maximise energy output and cut electricity costs in the long run. With their ability to perform in a range of conditions and their sleek appearance, they strike the perfect balance between performance and dependability.
Polycrystalline solar panels

Polycrystalline solar panels offer a more wallet-friendly option for homeowners looking to venture into solar energy. Here’s how these solar panels work and what they bring to the table:
- Poly panels are made from melting multiple silicon crystals, they have a distinct bluish hue and lower efficiency compared to monocrystalline solar panels.
- Their straightforward manufacturing process makes them more affordable, perfect for budget-conscious homeowners.
- Polycrystalline panels have efficiency rates of around 14%-16%. This means they require more roof space to generate the same power as their monocrystalline counterparts.
- They’re more sensitive to heat, losing efficiency quicker in hot climates.
- Despite being more affordable, they can still last up to 25 years, delivering long-term savings and durability.
For homes with plenty of roof space, polycrystalline panels strike a solid balance between cost savings and dependable energy production.
2nd Generation solar panels (thin-film technology)
Thin-film solar panels
Close-up of thin film solar panels mounted on roof. Thin film solar panels can cover more surface area, but won’t last as long as other types of solar panels (Fieldsken Ken Fields, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons).
Thin-film solar panels, also called amorphous cells, offer a flexible and innovative twist on traditional solar technology at an even cheaper price:
- Thin-film panels are lightweight and versatile, they can be seamlessly integrated into roofs, windows, or even vehicles.
- With lower efficiency (7%-13%) than monocrystalline or polycrystalline panels, thin-film solar panels need more surface area to generate the same amount of power.
- They perform well in both high temperatures and low-light conditions, making them a great fit for the UK’s unpredictable weather.
- Their lower upfront costs mean a quicker payback period, but they come with a shorter lifespan (10-20 years) and less durability compared to crystalline panels.
They’re ideal for projects requiring flexibility and affordability. Indubitably, thin-film panels deliver, even with their reduced efficiency.
3rd Generation solar panels (the next generation)
Third-generation solar panels represent the future of solar technology. They use advanced materials and techniques to increase overall efficiency, lower the costs, and offer much greater flexibility.
Here’s a glimpse into what the future of solar looks like:
Biohybrid solar panels
Biohybrid solar panels combine natural elements, like plant proteins, with synthetic materials to capture the sun’s incredible rays and turn it into green electricity. This essentially mimics photosynthesis.
Though still in the research phase, the biohybrid solar cell shows promise for being more efficient than traditional solar technology. It offers a greener and more innovative way to harness solar energy. However, they’re not yet available for commercial use.
Concentrated PV Cell (CPV and HCVP)
Concentrated PV (CPV) cells use lenses or mirrors to focus sunlight onto a small area. This boosts energy output with super-efficient solar cells. With efficiency rates over 40%, they’re much more powerful than standard panels.
High-Concentrated PV (HCVP) takes it a step further, using even more concentrated sunlight to produce even more energy. This makes it a great choice for those large-scale solar farms. However, they need direct sunlight to perform their best. So they’re perfect for areas with constant, strong sun exposure.
Perovskite solar panels
Perovskite solar panels are something truly impressive in the world of all things solar. They’re highly efficient and more affordable to produce than monocrystalline solar panels or polycrystalline solar panels. Thanks to their unique crystal structure, they capture sunlight amazingly well. Incredibly, lab tests are showing efficiencies of over 25%!
They have strong potential as an alternative to silicon-based panels. However, researchers are still working on making them more durable for long-term use. Once that’s sorted, perovskite panels could become a cost-effective, high-performance option for everyday solar energy.
Organic photovoltaics (OPVs)
Organic photovoltaics use lightweight, flexible materials like polymers to capture sunlight. Indeed, this makes them perfect for more unique applications like fabrics, portable devices, or even wearables. Unlike crystalline solar panels, they’re bendable and can adapt to a range of surfaces.
While they’re not as efficient as silicon-based panels just yet, their flexibility and affordability make them a pretty promising option for the creative and small-scale solar projects.
Quantum dot solar cells
Quantum dot solar cells use tiny semiconductor particles, called quantum dots, to absorb and emit light across different wavelengths. This helps them capture more of the sunlight. It also helps boost energy production.

Their versatility holds greater potential for improving solar efficiency. This is why researchers are looking into how they could be integrated into things like windows and other surfaces. Quantum dots could open the door to exciting new, highly efficient solar technologies in the future.
Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells (DSSCs)
Dye-sensitised solar cells (DSSCs) are a type of thin-film technology that use dye to capture the sun’s rays and turn it into electricity. While they’re not as efficient as crystalline solar panels, they’re much more flexible and cheaper to produce.
Their flexibility makes them ideal for specific uses like portable electronics or adding solar power to building materials where traditional rigid panels wouldn’t work as well.
Latest solar panels with innovative applications & technologies
Solar technology is evolving rapidly and ever-changing. This is giving us more flexible, efficient options for a variety of needs, like never before. Take a look at some of the most recent solar innovation technologies below:
Glass-glass solar panels
Glass-glass solar panels encase solar cells between two layers of glass, providing superior durability and protection. This design not only increases light transmission but also makes the panels more resistant to weather, UV rays, and physical damage.
Though they come with a higher price tag, their long lifespan and lower maintenance needs make them a smart investment. They’re perfect for homeowners and businesses looking for tough, long-lasting solar solutions. This is because they can handle harsh conditions while delivering maximum performance and efficiency.
Bifacial solar panels
Bifacial solar panels generate energy from both sides, capturing sunlight directly and from reflective surfaces like the ground. This clever design increases energy output by up to 30%. This makes their energy efficiency rating much better than crystalline solar panels.
While pricier, their enhanced efficiency allows them to generate more power in the same space, offering a great return on investment. This is especially the case in areas with reflective surfaces like snow or light-coloured roofs.
In-roof solar panels
In-roof solar panels, or Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV), are seamlessly built into your roof, offering a sleek, modern aesthetic. They blend beautifully with the roofline, cutting out the need for additional roofing materials and potentially lowering costs while keeping the weight down.
However, they may not produce nearly as much energy as traditional panels. So in this case, they’re really more about style and integration than maximum energy output.
Solar tiles are designed to resemble traditional roof tiles while generating electricity. Though less efficient than conventional panels, they provide a sleek, integrated look for homeowners who want a seamless design. They tend to be more expensive but deliver a modern, stylish appeal.

Transparent solar panels
Transparent solar panels allow light to pass through while generating electricity, making them perfect for windows, conservatories, canopies, and carports. This lets homeowners enjoy natural light while still producing energy. This tends to be a big plus for modern architectural designs.
While not as efficient as traditional panels yet, the technology here is steadily improving. Moreover, their performance is steadily increasing. However, due to their cutting-edge design, they come with a higher price tag. Additionally, they do require professional installation to ensure seamless integration.
Solar panels with PERC Technology
PERC (Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell) panels are designed with a special layer that reflects unused sunlight back into the cell, improving efficiency. They’re particularly effective on cloudy days when sunlight is more diffused. Although they have a higher upfront cost, their superior performance can lead to long-term savings.
Solar panels with TopCon Technology
TopCon (Tunnel Oxide Passivated Contact) technology pushes solar efficiency even further by enhancing light absorption and minimising energy loss. A thin oxide layer on the back of the cell captures more energy by reducing losses.
With their efficiency rates exceeding 23%, TopCon panels are some of the most efficient available as of now. They’re also more resistant to light-induced degradation, which means they last longer. Though they may cost more upfront, their long-term energy savings make them an increasingly popular choice in the market.
Choosing the best solar panel for your home
When choosing the best solar panel for your own home, it’s important to consider all the right factors. This way, you can make sure the system matches both your energy needs and personal preferences.
Factors to consider
When deciding on a solar panel, think about the way it looks, any upfront costs, and just how efficient it is:
- Monocrystalline solar panels stand out as the top pick: they deliver the highest power output, peak efficiency, and quickest payback. Plus, they do all this while looking sleek.
- Polycrystalline and thin-film panels are solid alternatives. This really just depends on your budget and energy demands.
How to select the right solar panel for your needs
- Think about your energy needs and budget when selecting a solar panel, use Soly’s online configurator to make things easier. You can calculate how many panels you need, how much electricity you produce, and how much you can save.
- Explore different panel types and their efficiency ratings.
- Talk to a solar expert to determine the best solution for your needs.
FAQ
What are the main types of solar panels?
There are three main types of solar panels: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film. At Soly, we specialise in monocrystalline panels from Jinko Solar because they offer the best in efficiency and durability. This makes them a solid long-term investment.
Which is the best solar panel type for home?
Monocrystalline solar panels are the best choice for homes, especially here in the UK. They’re super efficient, take up less space, and still work well on those cloudy, low-light days we’re so used to.
Which are the best solar panel type for commercial use?
Monocrystalline solar panels are perfect for commercial installations as they generate more power and are designed to last. They provide consistent, long-term energy solutions.
Which solar panel type is the most efficient?
Monocrystalline panels are the most efficient option because they convert more sunlight into electricity than other types of solar panels.
Which solar panel type has the highest power capacity?
Monocrystalline panels pack the most power into each square metre, which makes them the best option when you’ve got limited space but need a lot of energy.
Which solar panel type has the longest lifespan?
Monocrystalline panels are built to last, often going strong for over 25 years. At Soly, we back our panels with warranties of up to 25 years.
Which are the types of solar energy technologies?
There are two main types of solar energy technologies: Photovoltaic (PV), which turns sunlight into electricity, and Solar Thermal, which uses sunlight to produce heat. At Soly, we focus on photovoltaic solar systems to help power your home.
What are the types of solar panel systems?
The main types of solar systems are grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid. A grid-tied system connects straight to the national grid, while a hybrid system combines solar panels with a battery, letting you store extra energy for later use. With a hybrid setup, you still have the grid as a backup when needed.
What is the difference between Monocrystalline and Polycrystalline solar panels?
Monocrystalline panels are made from a single crystal of silicon. This gives them better efficiency and a stylish, modern look. On the other hand, polycrystalline panels are made from multiple silicon crystals. This makes them more budget-friendly but less efficient. At Soly, we focus on monocrystalline panels because they offer the best performance and are built to last.
Final Verdict: Which is the best type of solar panel?
Indubitably, there are several types of solar panels out there today, like monocrystalline, polycrystalline, thin-film, and some newer advanced options. Each has its own advantages, depending on your home, space, and budget.
Overall, monocrystalline panels continue to reign and stand out as the best option. This is thanks to their superior efficiency, sleek appearance, and long-term savings. However, if you’re on a tighter budget, polycrystalline and thin-film panels offer solid alternatives.
Of course, the future is bright and we can see from the advancements in solar technology that the ways to harness the power from the sun are only going up from here. However, it’s safe to say that the traditional options are something that we can continue to rely on, knowing that they will remain tried and tested.
To make sure you choose the best system for your needs, talk to a Soly solar expert for personalised advice.
Why choose Soly?
At Soly, we make switching to solar easy. Here’s what makes us different:
- We use Jinko Solar monocrystalline panels, known for high efficiency and energy savings.
- Rated 4.8 stars on Google, and 4.7-stars on TrustPilot, reflecting our commitment to customer satisfaction.
- Proud to be a Which? Trusted Trader, ensuring vetted, reliable, and accredited installers.
- Over 10 years of experience and 35,000+ happy customers globally.
- Our solar panels come with up to 25-year guarantees, ensuring long-term reliability.
- We provide top-tier service, making solar energy simple and effective for UK homeowners.
- We offer the best in financing options through Ideal 4 Finance and our £500 deposit option with final payment only due when the system is up and running.
Contact our solar experts today to see how we can help you start harnessing the power of the sun’s rays!